Representation of Binary Tree
- Types of Representation of Binary Tree
- Static Representation of Binary Tree.
- Dynamic Representation of Binary Tree.
⩥Static Representation of Binary Tree.
- The element are stroed in the array level-wise starting from the root. Since a full binary tree with total 'd' levels will have maximum of 2d-1 nodes, we can use an array od size 2d-1 to represrnt the binary tree.
- This representation allows random access to any node.
- The ith node is at location i where (0<=i<n).
- Find Parent of Node:- The parent of node is at location (i-1)/2. (i=0 is the root has no parent).
= (i-1)/2 = (i-1)/2
= (4-1)/2 = (5-1)/2
= 3/2 = 4/2
= 1 i.e B parent of E. = 2 i.e. C is parent of F.
3. Find Left Child:- Left child of a node at position 2i+1. If (2i+1)>=n(n = size array), then 'i ' doesn't have a left child.
i=1(B) i=5(F)
= 2i+1 = 2i+1
= 2*1+1 = 2*5+1
= 2+1 = 10+1
= 3 i.e. 'D' is left child of 'B'. = 11 i.e. 11>10(size of array) so 'F' doesn't have left child.
4. Find Right Child:- Right child of node i is at position 2i+2. If (2i+2) >=n(n = size array), then 'i' doesn't have right child.
i=1(B) i=6(G)
= 2i+2 = 2i+2
= 2*1+2 = 2*6+2
= 4 i.e. 'E' is right child of B. = 14 .e. 14>10(size of array) so 'G' doesn't have right child.
- Advantages of Static Representation of Binary Tree
- This is simple representation of tree.
- It gives complete information about the tree.
- Any element can be easily located in time. O(1) by calculation.
- Memory efficient if the tree is perfect or complete binary tree.
- Tree operations such as search can be performed efficiently.
- Disadvantages Static Representation of Binary Tree
- Since an array is used, there is alimitation on its size.
- Nodes can't be inserted or deleted easily.
- If the tree is not full or complete binary tree, a lot of memory will be wasted since many array elements will be vacant.
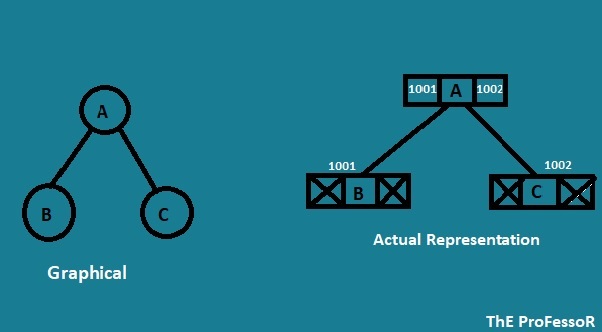
⩥Dynamic Representation of Binary Tree.
- This linked representation of a tree using the dynamic memory allocation.
- The tree is a linked set of noedes.
- Each node stores the nodes value element and links to its left and right childern.
- Node Structure
{
struct node *left;
int info;
struct node *right;
}NODE;
>>The root is an external pointer to the topmost node in the tree.
NODE * root; //declared root
- Advantages of Dynamic Representation of Binary Tree
- Efficient representation of any type of binary tree.
- Nodes can be easily inserted and deleted.
- Since dynamic memory allocation is used is used, memory is not wasted.
- Disadvantages Dynamic Representation of Binary Tree
- Each node requires additional memory o store pointers.
- A node can't be accessed directly. Nodes can be accessed only sequentially using the links stating from the root.
- More complex compared to static repersentation.


Comments
Post a Comment